在Unix/Linux系统中,root用户帐户是超级用户帐户,因此它可以用来做系统上可以实现的任何事情。然而,这在很多方面都是非常危险的行为。一个可能是root用户可能输入错误的命令并破坏整个系统,或者攻击者获得了root用户帐户的访问权限并控制了整个系统。
基于这样的背景,在Ubuntu及Ubuntu衍生版中,root用户账户默认是被锁定的,普通用户(无论是否是系统管理员)只能通过sudo命令获得超级用户权限。Ubuntu系统管理员可能发生的最糟糕的事情之一就是失去使用sudo命令的权限,这种情况通常被称为“broken sudo”,这绝对是毁灭性的后果。
broken sudo可能由以下任何原因引起:
- 不应从sudo或admin组中删除用户。
- /etc/sudoers文件被更改以防止sudo或admin组中的用户使用sudo命令将他们的权限提升到root的权限。
- /etc/sudoers文件的权限未设置为0440。
为了在你的系统上执行关键任务,例如查看或更改重要的系统文件,或更新系统,需要sudo命令以获得超级用户权限。如果由于上面提到的一种或多种原因而拒绝使用sudo ,应该怎么办?下图显示了阻止默认系统用户运行sudo命令的情况:
ecscoupon@Ecscoupon ~ $ sudo visudo [ sudo ] password for aaronkilik: aaronkilik is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported. ecscoupon@Ecscoupon ~ $ sudo apt install vim [ sudo ] password for aaronkilik: aaronkilik is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported.
如何在Ubuntu中修复损坏的sudo命令
如果你碰巧在系统上只运行Ubuntu,则在开机后,按住该Shift键几秒钟以获取Grub引导菜单。此外,如果你正在运行双引导(Ubuntu与Windows或Mac OS X),那么默认情况下应该会看到Grub引导菜单。使用Down Arrow选择“Advanced options for Ubuntu”并按Enter键:
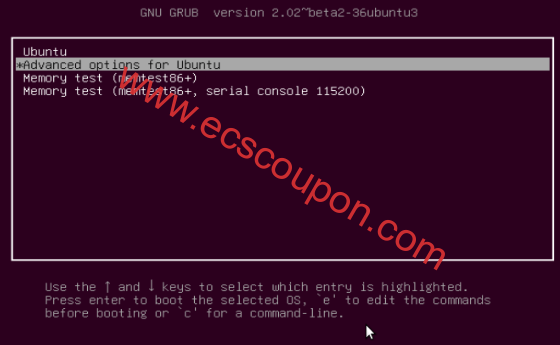
这样将在下面的界面中,选择带有“ recovery mode ”选项的内核,然后按Enter进入“ Recovery menu ”,如下图所示:

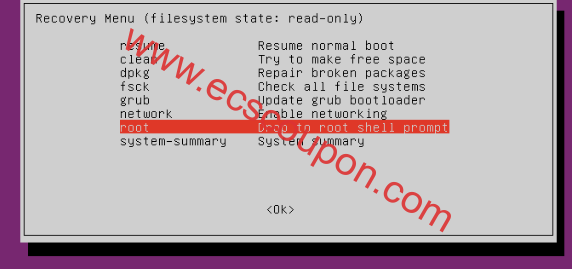
下面是“ Recovery menu ”,表示root文件系统挂载为只读。移至“ root Drop to root shell prompt ”行,然后按Enter键进行维护操作,如下图所示:
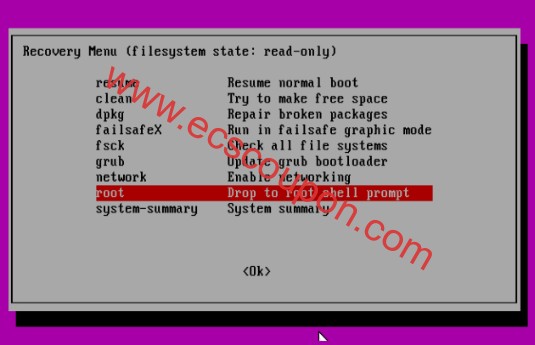
此时,你应该处于root shell提示符下。正如我们之前所见,文件系统以只读方式挂载,因此,要对系统进行更改,需要通过运行以下命令以读/写方式重新挂载:
# mount -o rw,remount /
示例方案1–将用户添加到sudo或admin组
假设用户已从sudo组中删除,要将用户添加回sudo组,请输入以下命令:
# adduser username sudo
注意:请记住使用系统上的实际用户名,在本文例子中,它是aaronkilik,如下图所示:

或者,在用户已从管理员组中删除的情况下,运行以下命令:
# adduser username admin
示例方案2–向用户授予sudo权限
假设/etc/sudoers文件被更改以防止sudo或admin组中的用户将他们的权限提升到超级用户的权限,然后按如下方式备份sudoers文件:
# cp /etc/sudoers /etc/sudoers.orginal
随后,打开sudoers文件,命令如下:
# visudo
并添加以下内容:
# # This file MUST be edited with the 'visudo' command as root. # # Please consider adding local content in /etc/sudoers.d/ instead of # directly modifying this file. # # See the man page for details on how to write a sudoers file. # Defaults env_reset Defaults mail_badpass Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbi$ # Host alias specification # User alias specification # Cmnd alias specification # User privilege specification root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL # Members of the admin group may gain root privileges %admin ALL=(ALL) ALL # Allow members of group sudo to execute any command %sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL # See sudoers(5) for more information on "#include" directives: #includedir /etc/sudoers.d
示例方案3–为sudoers文件设置正确的权限
假设/etc/sudoers文件的权限没有设置为0440,那么运行如下命令修改:
# chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers
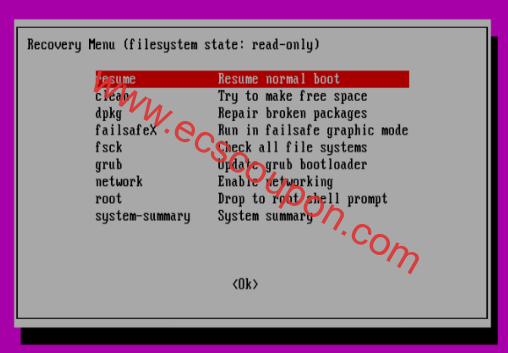
最后但同样重要的是,在运行所有必要的命令后,键入命令exit返回“恢复菜单”:
# exit
使用向下箭头选择<Ok>并按Enter:
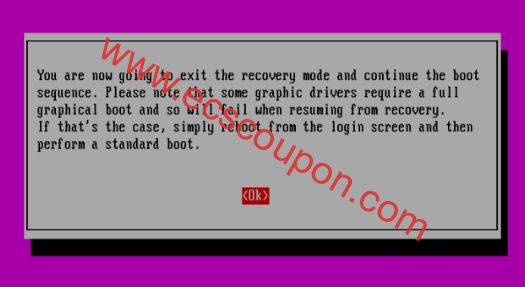
按<Ok>以继续正常启动顺序:
总结
以上这种方法应该还是比较实用的,特别是当涉及到管理用户帐户时,除了使用恢复模式别无选择。当然,上述方法仅供参考,也不是100%适合每个人,所以区别对待具体的问题。
 趣云笔记
趣云笔记